Page 83 - A Practical Guide from Design Planning to Manufacturing
P. 83
Computer Components 59
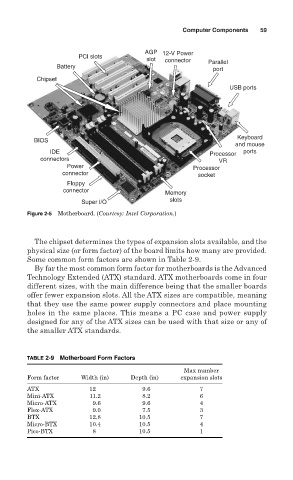
AGP 12-V Power
PCI slots
slot connector Parallel
Battery port
Chipset
USB ports
Keyboard
BIOS
and mouse
IDE Processor ports
connectors VR
Power Processor
connector socket
Floppy
connector
Memory
Super I/O slots
Figure 2-5 Motherboard. (Courtesy: Intel Corporation.)
The chipset determines the types of expansion slots available, and the
physical size (or form factor) of the board limits how many are provided.
Some common form factors are shown in Table 2-9.
By far the most common form factor for motherboards is the Advanced
Technology Extended (ATX) standard. ATX motherboards come in four
different sizes, with the main difference being that the smaller boards
offer fewer expansion slots. All the ATX sizes are compatible, meaning
that they use the same power supply connectors and place mounting
holes in the same places. This means a PC case and power supply
designed for any of the ATX sizes can be used with that size or any of
the smaller ATX standards.
TABLE 2-9 Motherboard Form Factors
Max number
Form factor Width (in) Depth (in) expansion slots
ATX 12 9.6 7
Mini-ATX 11.2 8.2 6
Micro-ATX 9.6 9.6 4
Flex-ATX 9.0 7.5 3
BTX 12.8 10.5 7
Micro-BTX 10.4 10.5 4
Pico-BTX 8 10.5 1