Page 349 - Microsensors, MEMS and Smart Devices - Gardner Varadhan and Awadelkarim
P. 349
ACOUSTIC WAVE PROPAGATION 329
x\-direction) has only an x2-component and is given by the following equation (see Auld
1973a,b):
u 2= wo cos — I x 2 + - J exp[j (cat - p nx\)] (10.30)
where b is the plate thickness, u 2 is the particle displacement at the surface, n is the
transverse modal index (0,1,2,3...), and t is time. The exponential term in the equation
describes the propagation of the displacement profile down the length of the waveguide
(along the x 1 -direction) with angular frequency w and wave number B n given by
(10.31)
where VQ is the unperturbed propagation velocity of the lowest-order mode.
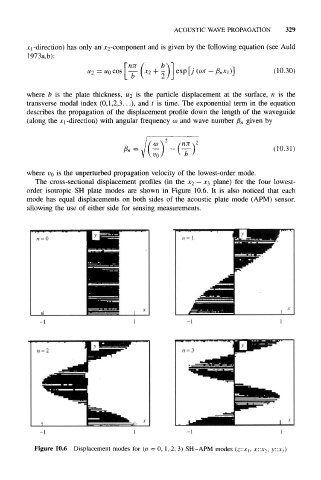
The cross-sectional displacement profiles (in the x 2 — x 3 plane) for the four lowest-
order isotropic SH plate modes are shown in Figure 10.6. It is also noticed that each
mode has equal displacements on both sides of the acoustic plate mode (APM) sensor,
allowing the use of either side for sensing measurements.
Figure 10.6 Displacement modes for (n = 0, 1, 2, 3) SH-APM modes (z::x 1 , x 2: y::x 3)