Page 209 - Modelling in Transport Phenomena A Conceptual Approach
P. 209
7.3. CONSERVATION OF TOTAL MASS 189
Case (ii) Liquid level in the tank decreases
The liquid level in the tank decreases, i.e., dhldt < 0 in Eq. (7), if
f-2' < H/2 (15)
Equation (12) is also valid for this case. Equations (9) and (15) imply that h, <
H/2. Since h, cannot be negative, this further implies that it is impossible to empty
the tank under these circumstances. The time required for the level of the tank to
reach 99% of the steady-state value is also given by Eq. (14).
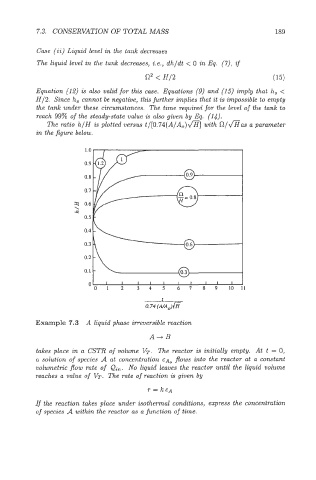
The ratio h/H is plotted versus t/[O.74(A/A0)a] with f-2/&as a parameter
in the figure below.
1
t
0.74 (ALAJ
Example 7.3 A liquid phase irreversible reaction
A+B
takes place in a CSTR of volume V,. The reactor is initially empty. At t = 0,
a solution of species A at concentration CA, jlows into the reactor at a constant
volumetric flow rate of Qj,. No liquid leaves the reactor until the liquid volume
reaches a value of VT. The rate of reaction is given by
r=kCA
If the reaction takes place under isothermal conditions, express the concentration
of species A within the reactor as a function of time.