Page 281 - Modelling in Transport Phenomena A Conceptual Approach
P. 281
8.2. ENERGY TRANSPORT WITHOUT CONVECTION 261
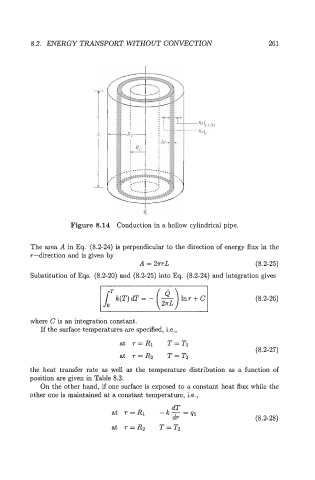
Figure 8.14 Conduction in a hollow cylindrical pipe.
The axea A in Eq. (8.2-24) is perpendicular to the direction of energy flux in the
r-direction and is given by
A = 2~rL (8.2-25)
Substitution of Eqs. (8.2-20) and (8.2-25) into Eq. (8.2-24) and integration gives
(8.2-26)
where C is an integration constant.
If the surface temperatures are specified, i.e.,
at r=R1 T=T1
(8.2-27)
at r= R2 T=T2
the heat transfer rate as well as the temperature distribution as a function of
position are given in Table 8.3.
On the other hand, if one surface is exposed to a constant heat flux while the
other one is maintained at a constant temperature, i.e.,
dT
at r=R1 -k-= 41
dr (8.2-28)
at r=Rz T=Tz