Page 316 - Modelling in Transport Phenomena A Conceptual Approach
P. 316
296 CHAPTER 8. STEADY MICROSCOPIC BALANCES WITHOUT GEN.
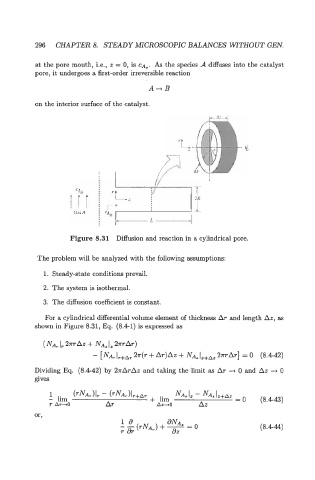
at the pore mouth, i.e., z = 0, is CA,. As the species A diffuses into the catalyst
pore, it undergoes a first-order irreversible reaction
A-+B
on the interior surface of the catalyst.
I TI
Gas A
Figure 8.31 Diffusion and reaction in a cylindrical pore.
The problem will be analyzed with the following assumptions:
1. Steady-state conditions prevail.
2. The system is isothermal.
3. The diffusion coefficient is constant.
For a cylindrical differential volume element of thickness AT and length Az, as
shown in Figure 8.31, Eq. (8.41) is expressed as
( NA, lr 27rrAz + NA, 1% ~~FTAT)
- [ NA, 2n(r + AT)Az + NA, [%+Ax ~TTAT] = 0 (8.442)
Dividing Eq. (8.442) by 2nArAz and taking the limit as AT + 0 and Az -+ 0
gives
1 (‘NArIIr - (TNAr)Ir+Ar + lim NAz 1% - NA, [%+A=
- lim =O (8.443)
T Ar+O AT Az-4 A2
dNAZ
Id
- - (TNA,) + - (8.444)
0
=
T ar dz