Page 58 - Modelling in Transport Phenomena A Conceptual Approach
P. 58
PROBLEMS 39
This further implies that the molar average velocity is equal to the volume average
velocity when the total molar concentration is constant.
2.12 For a gas at constant pressure, why does the Schmidt number usually remain
fairly constant over a large temperature range, whereas the diffusion coefficient
changes markedly?
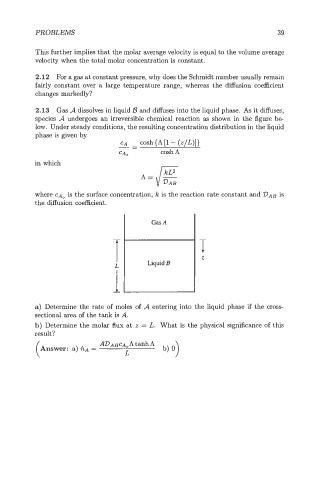
2.13 Gas A dissolves in liquid B and diffuses into the liquid phase. As it diffuses,
species A undergoes an irreversible chemical reaction as shown in the figure be
low. Under steady conditions, the resulting concentration distribution in the liquid
phase is given by
CA
-- - cosh(A[l- (z/L)]}
CA, cash A
in which
where CA, is the surface concentration, k is the reaction rate constant and VAB is
the diffusion coefficient.
a) Determine the rate of moles of A entering into the liquid phase if the cross-
sectional area of the tank is A.
b) Determine the molar flux at z = L. What is the physical significance of this
result?
A
AVABCA, tanh A
=
Answer: a) jl~
L