Page 142 -
P. 142
4 Dynamic Workflow 131
The fundamental feature of RDR is that it avoids the difficulties inherent in
attempting to precompile a systematic understanding, organization, and assembly
of all knowledge in a particular domain. The RDR method is well established and
fully formalized and has been implemented as the basis for a variety of commercial
applications, including systems for reporting DNA test results, environmental test-
ing, intelligent document retrieval, fraud detection based on patterns of behavior,
personal information management, and data mining of large and complex data sets.
The Worklet Service uses RDR to define rules that allow the correct worklet to be
chosen from a repertoire of available worklets for a given task in a process instance,
using the particular context of the instance.
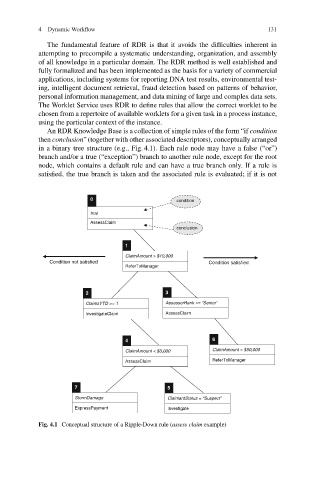
An RDR Knowledge Base is a collection of simple rules of the form “if condition
then conclusion” (together with other associated descriptors), conceptually arranged
in a binary tree structure (e.g., Fig. 4.1). Each rule node may have a false (“or”)
branch and/or a true (“exception”) branch to another rule node, except for the root
node, which contains a default rule and can have a true branch only. If a rule is
satisfied, the true branch is taken and the associated rule is evaluated; if it is not
0 condition
true
AssessClaim
conclusion
1
ClaimAmount > $10,000
Condition not satisfied Condition satisfied
ReferToManager
2 3
ClaimsYTD >= 1 AssessorRank >= “Senior”
InvestigateClaim AssessClaim
4 6
ClaimAmount < $3,000 ClaimAmount > $50,000
AssessClaim ReferToManager
7 5
StormDamage ClaimantStatus = “Suspect”
ExpressPayment Investigate
Fig. 4.1 Conceptual structure of a Ripple-Down rule (assess claim example)