Page 150 -
P. 150
4 Dynamic Workflow 139
4.8 Secondary Data Sources
When making a contextual choice of an appropriate worklet, it may be desirable or
even necessary to seek data outside the parameters of the task/or case. For example,
the current state of the process, or the states of individual tasks, may have some
bearing on the choices made; available resources may be an important factor and
so on. Thus, choosing the most appropriate worklet for a situation will be achieved
by defining rules that use a combination of currently available data attribute values,
both case-dependent and independent.
One method of accessing the current set of states for an instantiated process,
resource data, and archival histories of previous instantiations of a specification may
be deduced by mining the process log file. A series of predicates can be constructed
to enable the extraction of the current state set and any relations between active
worklets and tasks, as well as archival trends and relations. These predicates may
then be used to augment the conditionals in RDR nodes to enable selection of the
most appropriate worklet.
The kinds of information that may be extracted from the process log file using
these predicates include the current status of a worklet, whether a worklet is a parent
or child of another worklet, when a certain state was entered or exited for a particular
worklet or task, the resource that triggered a state change, and so on. Chapter 11
provides an explanation of how such predicates may be constructed and used in
practice.
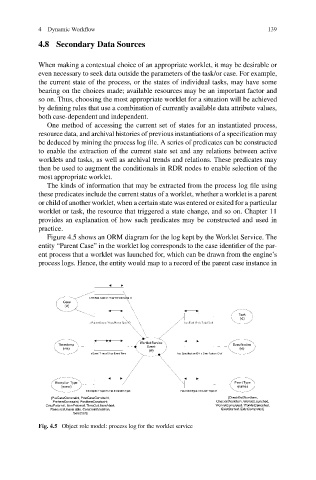
Figure 4.5 shows an ORM diagram for the log kept by the Worklet Service. The
entity “Parent Case” in the worklet log corresponds to the case identifier of the par-
ent process that a worklet was launched for, which can be drawn from the engine’s
process logs. Hence, the entity would map to a record of the parent case instance in
Fig. 4.5 Object role model: process log for the worklet service