Page 194 -
P. 194
6 Declarative Workflow 185
name ... ... ... existence ... ...
TEMPLATES graphical ... ... ... 1..* ... ...
<> A
LTL
...
...
...
...
...
A
CONSTRAINTS semantics graphical <> Arrange Delivery Appointment Create Bill of Lading
<> Create Bill of Lading
1..*
1..*
Arrange Delivery
Appointment
1..*
1..*
MODELS Arrange Pickup Arrange Delivery Create Shipment Appointment Create Bill of lading
Arrange Delivery
1..*
Appointment
1..*
1..*
Appointment
Information Document
Arrange Pickup
Appointment precedence
Truck Load Less Than Truck Load
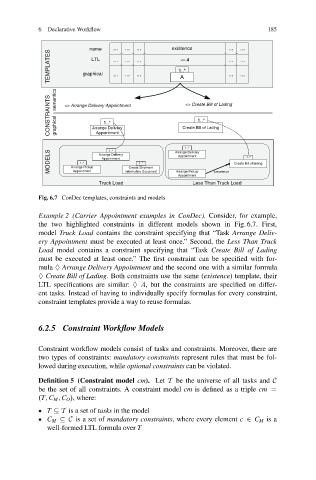
Fig. 6.7 ConDec templates, constraints and models
Example 2 (Carrier Appointment examples in ConDec). Consider, for example,
the two highlighted constraints in different models shown in Fig. 6.7. First,
model Truck Load contains the constraint specifying that “Task Arrange Deliv-
ery Appointment must be executed at least once.” Second, the Less Than Truck
Load model contains a constraint specifying that “Task Create Bill of Lading
must be executed at least once.” The first constraint can be specified with for-
mula ♦ Arrange Delivery Appointment and the second one with a similar formula
♦ Create Bill of Lading. Both constraints use the same (existence) template, their
LTL specifications are similar: ♦ A, but the constraints are specified on differ-
ent tasks. Instead of having to individually specify formulas for every constraint,
constraint templates provide a way to reuse formulas.
6.2.5 Constraint Workflow Models
Constraint workflow models consist of tasks and constraints. Moreover, there are
two types of constraints: mandatory constraints represent rules that must be fol-
lowed during execution, while optional constraints can be violated.
Definition 5 (Constraint model cm). Let T be the universe of all tasks and C
be the set of all constraints. A constraint model cm is defined as a triple cm D
.T; C M ; C O /,where:
T T is a set of tasks in the model
C M C is a set of mandatory constraints, where every element c 2 C M is a
well-formed LTL formula over T