Page 197 -
P. 197
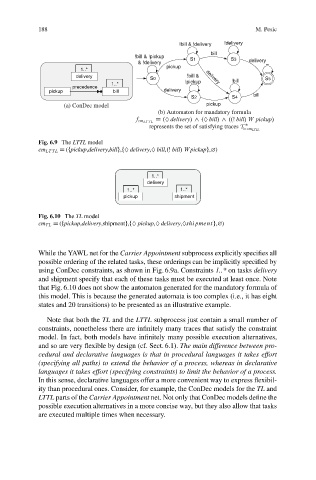
188 M. Pesic
!bill & !delivery !delivery
bill
!bill & !pickup
S1 S3 delivery
& !delivery –
pickup
1..*
delivery !bill &
S0 delivery !bill S5
1..* !pickup
precedence
pickup bill delivery
S2 S4 bill
(a) ConDec model pickup
(b) Automaton for mandatory formula
D .♦ delivery/ ^ .♦ bill/ ^ ..Š bill/W pickup/
f cm LT TL
represents the set of satisfying traces T
cm LTTL
Fig. 6.9 The LTTL model
cm LT TL D (fpickup,delivery,billg,f♦ delivery,♦ bill,.Š bill/W pickupg,∅)
1..*
delivery
1..* 1..*
pickup shipment
Fig. 6.10 The TL model
cm TL D (fpickup,delivery,shipmentg,f♦ pickup,♦ delivery,♦shipmentg,∅)
While the YAWL net for the Carrier Appointment subprocess explicitly specifies all
possible ordering of the related tasks, these orderings can be implicitly specified by
using ConDec constraints, as shown in Fig. 6.9a. Constraints 1..* on tasks delivery
and shipment specify that each of these tasks must be executed at least once. Note
that Fig. 6.10 does not show the automaton generated for the mandatory formula of
this model. This is because the generated automata is too complex (i.e., it has eight
states and 20 transitions) to be presented as an illustrative example.
Note that both the TL and the LTTL subprocess just contain a small number of
constraints, nonetheless there are infinitely many traces that satisfy the constraint
model. In fact, both models have infinitely many possible execution alternatives,
and so are very flexible by design (cf. Sect. 6.1). The main difference between pro-
cedural and declarative languages is that in procedural languages it takes effort
(specifying all paths) to extend the behavior of a process, whereas in declarative
languages it takes effort (specifying constraints) to limit the behavior of a process.
In this sense, declarative languages offer a more convenient way to express flexibil-
ity than procedural ones. Consider, for example, the ConDec models for the TL and
LTTL parts of the Carrier Appointment net. Not only that ConDec models define the
possible execution alternatives in a more concise way, but they also allow that tasks
are executed multiple times when necessary.