Page 272 -
P. 272
268 M. Adams
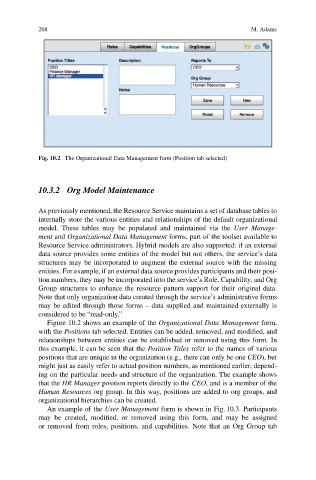
Fig. 10.2 The Organizational Data Management form (Position tab selected)
10.3.2 Org Model Maintenance
As previously mentioned, the Resource Service maintains a set of database tables to
internally store the various entities and relationships of the default organizational
model. These tables may be populated and maintained via the User Manage-
ment and Organizational Data Management forms, part of the toolset available to
Resource Service administrators. Hybrid models are also supported: if an external
data source provides some entities of the model but not others, the service’s data
structures may be incorporated to augment the external source with the missing
entities. For example, if an external data source provides participants and their posi-
tion numbers, they may be incorporated into the service’s Role, Capability, and Org
Group structures to enhance the resource pattern support for their original data.
Note that only organization data created through the service’s administrative forms
may be edited through those forms – data supplied and maintained externally is
considered to be “read-only.”
Figure 10.2 shows an example of the Organizational Data Management form,
with the Positions tab selected. Entities can be added, removed, and modified, and
relationships between entities can be established or removed using this form. In
this example, it can be seen that the Position Titles refer to the names of various
positions that are unique in the organization (e.g., there can only be one CEO), but
might just as easily refer to actual position numbers, as mentioned earlier, depend-
ing on the particular needs and structure of the organization. The example shows
that the HR Manager position reports directly to the CEO, and is a member of the
Human Resources org group. In this way, positions are added to org groups, and
organizational hierarchies can be created.
An example of the User Management form is shown in Fig. 10.3. Participants
may be created, modified, or removed using this form, and may be assigned
or removed from roles, positions, and capabilities. Note that an Org Group tab