Page 53 -
P. 53
40 N. Russell and A. ter Hofstede
control-flow control-flow
X: X: X: data flow (value of X) common data store data flow (value of X)
& data flow & data flow
X:
X: X:
control-flow control-flow
data flow (value of X)
X: control-flow control-flow X:
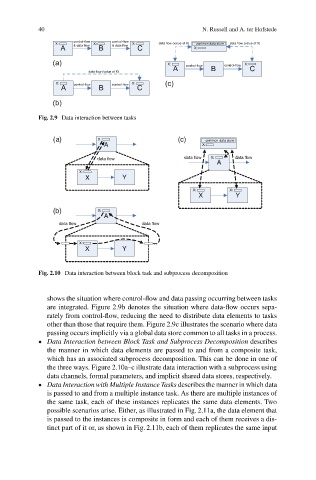
Fig. 2.9 Data interaction between tasks
(a) X: (c) common data store
A X:
data flow data flow X: data flow
A
X:
X Y
X: X:
X Y
(b) X:
A
data flow data flow
X:
X Y
Fig. 2.10 Data interaction between block task and subprocess decomposition
shows the situation where control-flow and data passing occurring between tasks
are integrated. Figure 2.9b denotes the situation where data-flow occurs sepa-
rately from control-flow, reducing the need to distribute data elements to tasks
other than those that require them. Figure 2.9c illustrates the scenario where data
passing occurs implicitly via a global data store common to all tasks in a process.
Data Interaction between Block Task and Subprocess Decomposition describes
the manner in which data elements are passed to and from a composite task,
which has an associated subprocess decomposition. This can be done in one of
the three ways. Figure 2.10a–c illustrate data interaction with a subprocess using
data channels, formal parameters, and implicit shared data stores, respectively.
Data Interaction with Multiple Instance Tasks describes the manner in which data
is passed to and from a multiple instance task. As there are multiple instances of
the same task, each of these instances replicates the same data elements. Two
possible scenarios arise. Either, as illustrated in Fig. 2.11a, the data element that
is passed to the instances is composite in form and each of them receives a dis-
tinct part of it or, as shown in Fig. 2.11b, each of them replicates the same input