Page 57 -
P. 57
44 N. Russell and A. ter Hofstede
start (R)
offer (S) offered to a suspended
single allocate (R)
resource
suspend (R) resume (R)
allocated to a
allocate (S) start (R) complete (R)
created single started completed
resource
fail (R)
allocate (R)
offered to
offer (S)
multiple start (R) failed
resources
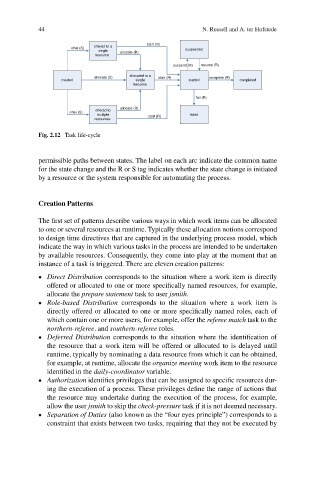
Fig. 2.12 Task life-cycle
permissible paths between states. The label on each arc indicate the common name
for the state change and the R or S tag indicates whether the state change is initiated
by a resource or the system responsible for automating the process.
Creation Patterns
The first set of patterns describe various ways in which work items can be allocated
to one or several resources at runtime. Typically these allocation notions correspond
to design time directives that are captured in the underlying process model, which
indicate the way in which various tasks in the process are intended to be undertaken
by available resources. Consequently, they come into play at the moment that an
instance of a task is triggered. There are eleven creation patterns:
Direct Distribution corresponds to the situation where a work item is directly
offered or allocated to one or more specifically named resources, for example,
allocate the prepare statement task to user jsmith.
Role-based Distribution corresponds to the situation where a work item is
directly offered or allocated to one or more specifically named roles, each of
which contain one or more users, for example, offer the referee match task to the
northern-referee.and southern-referee roles.
Deferred Distribution corresponds to the situation where the identification of
the resource that a work item will be offered or allocated to is delayed until
runtime, typically by nominating a data resource from which it can be obtained,
for example, at runtime, allocate the organize meeting work item to the resource
identified in the daily-coordinator variable.
Authorization identifies privileges that can be assigned to specific resources dur-
ing the execution of a process. These privileges define the range of actions that
the resource may undertake during the execution of the process, for example,
allow the user jsmith to skip the check-pressure task if it is not deemed necessary.
Separation of Duties (also known as the “four eyes principle”) corresponds to a
constraint that exists between two tasks, requiring that they not be executed by