Page 72 - Modern Control Systems
P. 72
46 Chapter 1 Introduction to Control Systems
over 800 m with more than 160 stories.There are 57 ele-
vators servicing this tallest free-standing structure in
the world. Traveling at up to 10 m/s, the elevators have
the world's longest travel distance from lowest to
highest stop. Describe a closed-loop feedback control
system that guides an elevator of a high-rise building
to a desired floor while maintaining a reasonable tran-
sit time [95]. Remember that high accelerations will
make the passengers uncomfortable.
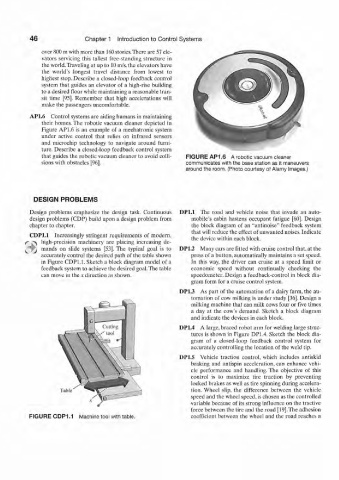
AP1.6 Control systems are aiding humans in maintaining
their homes. The robotic vacuum cleaner depicted in
Figure API.6 is an example of a mechatronic system
under active control that relies on infrared sensors
and microchip technology to navigate around furni-
ture. Describe a closed-loop feedback control system
that guides the robotic vacuum cleaner to avoid colli- FIGURE AP1.6 A robotic vacuum cleaner
sions with obstacles [96]. communicates with the base station as it maneuvers
around the room. (Photo courtesy of Alamy Images.)
DESIGN PROBLEMS
Design problems emphasize the design task. Continuous DPl.l The road and vehicle noise that invade an auto-
design problems (CDP) build upon a design problem from mobile's cabin hastens occupant fatigue [60]. Design
chapter to chapter. the block diagram of an "antinoise" feedback system
that will reduce the effect of unwanted noises. Indicate
CDP1.1 Increasingly stringent requirements of modern,
rc\ high-precision machinery are placing increasing de- the device within each block.
v '"YJ mands on slide systems [53]. The typical goal is to DP1.2 Many cars are fitted with cruise control that, at the
accurately control the desired path of the table shown press of a button, automatically maintains a set speed.
in Figure CDP1.1. Sketch a block diagram model of a In this way, the driver can cruise at a speed limit or
feedback system to achieve the desired goal. The table economic speed without continually checking the
can move in the x direction as shown. speedometer. Design a feedback-control in block dia-
gram form for a cruise control system.
DP1.3 As part of the automation of a dairy farm, the au-
tomation of cow milking is under study [36]. Design a
milking machine that can milk cows four or five times
a day at the cow's demand. Sketch a block diagram
and indicate the devices in each block.
DP1.4 A large, braced robot arm for welding large struc-
tures is shown in Figure DPI.4. Sketch the block dia-
gram of a closed-loop feedback control system for
accurately controlling the location of the weld tip.
DP1.S Vehicle traction control, which includes antiskid
braking and antispin acceleration, can enhance vehi-
cle performance and handling. The objective of this
control is to maximize tire traction by preventing
locked brakes as well as tire spinning during accelera-
tion. Wheel slip, the difference between the vehicle
speed and the wheel speed, is chosen as the controlled
variable because of its strong influence on the tractive
force between the lire and the road [19]. The adhesion
FIGURE CDP1.1 Machine tool with table. coefficient between the wheel and the road reaches a