Page 270 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 270
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 127
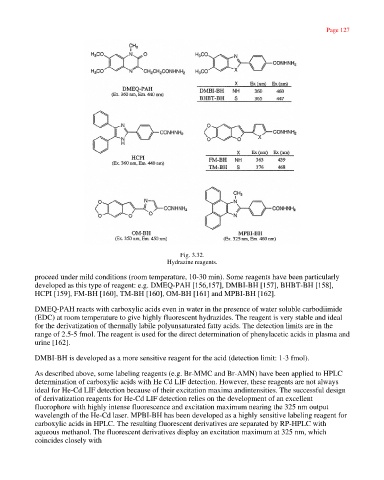
Fig. 3.32.
Hydrazine reagents.
proceed under mild conditions (room temperature, 10-30 min). Some reagents have been particularly
developed as this type of reagent: e.g. DMEQ-PAH [156,157], DMBI-BH [157], BHBT-BH [158],
HCPI [159], FM-BH [160], TM-BH [160], OM-BH [161] and MPBI-BH [162].
DMEQ-PAH reacts with carboxylic acids even in water in the presence of water soluble carbodiimide
(EDC) at room temperature to give highly fluorescent hydrazides. The reagent is very stable and ideal
for the derivatization of thermally labile polyunsaturated fatty acids. The detection limits are in the
range of 2.5-5 fmol. The reagent is used for the direct determination of phenylacetic acids in plasma and
urine [162].
DMBI-BH is developed as a more sensitive reagent for the acid (detection limit: 1-3 fmol).
As described above, some labeling reagents (e.g. Br-MMC and Br-AMN) have been applied to HPLC
determination of carboxylic acids with He Cd LIF detection. However, these reagents are not always
ideal for He-Cd LIF detection because of their excitation maxima andintensities. The successful design
of derivatization reagents for He-Cd LIF detection relies on the development of an excellent
fluorophore with highly intense fluorescence and excitation maximum nearing the 325 nm output
wavelength of the He-Cd laser. MPBI-BH has been developed as a highly sensitive labeling reagent for
carboxylic acids in HPLC. The resulting fluorescent derivatives are separated by RP-HPLC with
aqueous methanol. The fluorescent derivatives display an excitation maximum at 325 nm, which
coincides closely with
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_127.ht... 30/09/2003