Page 93 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 93
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 38
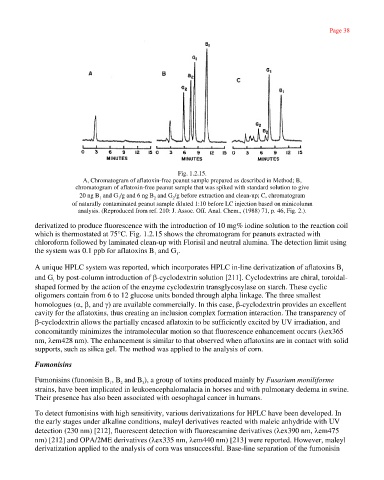
Fig. 1.2.15.
A, Chromatogram of aflatoxin-free peanut sample prepared as described in Method; B,
chromatogram of aflatoxin-free peanut sample that was spiked with standard solution to give
20 ng B and G /g and 6 ng B and G /g before extraction and clean-up; C, chromatogram
1 1 2 2
of naturally contaminated peanut sample diluted 1:10 before LC injection based on minicolumn
analysis. (Reproduced from ref. 210: J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., (1988) 71, p. 46, Fig. 2.).
derivatized to produce fluorescence with the introduction of 10 mg% iodine solution to the reaction coil
which is thermostated at 75°C. Fig. 1.2.15 shows the chromatogram for peanuts extracted with
chloroform followed by laminated clean-up with Florisil and neutral alumina. The detection limit using
the system was 0.1 ppb for aflatoxins B and G .
1
1
A unique HPLC system was reported, which incorporates HPLC in-line derivatization of aflatoxins B
1
and G by post-column introduction of β-cyclodextrin solution [211]. Cyclodextrins are chiral, toroidal-
1
shaped formed by the action of the enzyme cyclodextrin transglycosylase on starch. These cyclic
oligomers contain from 6 to 12 glucose units bonded through alpha linkage. The three smallest
homologues (α, β, and γ) are available commercially. In this case, β-cyclodextrin provides an excellent
cavity for the aflatoxins, thus creating an inclusion complex formation interaction. The transparency of
β-cyclodextrin allows the partially encased aflatoxin to be sufficiently excited by UV irradiation, and
concomitantly minimizes the intramolecular motion so that fluorescence enhancement occurs (λex365
nm, λem428 nm). The enhancement is similar to that observed when aflatoxins are in contact with solid
supports, such as silica gel. The method was applied to the analysis of corn.
Fumonisins
Fumonisins (funonisin B , B and B ), a group of toxins produced mainly by Fusarium moniliforme
3
2
1
strains, have been implicated in leukoencephalomalacia in horses and with pulmonary dedema in swine.
Their presence has also been associated with oesophagal cancer in humans.
To detect fumonisins with high sensitivity, various derivatizations for HPLC have been developed. In
the early stages under alkaline conditions, maleyl derivatives reacted with maleic anhydride with UV
detection (230 nm) [212], fluorescent detection with fluorescamine derivatives (λex390 nm, λem475
nm) [212] and OPA/2ME derivatives (λex335 nm, λem440 nm) [213] were reported. However, maleyl
derivatization applied to the analysis of corn was unsuccessful. Base-line separation of the fumonisin
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_38.html 30/09/2003