Page 97 - Modern Derivatization Methods for Separation Sciences
P. 97
Document Página 1 de 2
Page 40
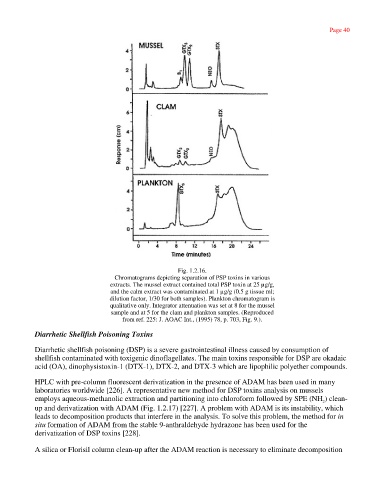
Fig. 1.2.16.
Chromatograms depicting separation of PSP toxins in various
extracts. The mussel extract contained total PSP toxin at 25 µg/g,
and the calm extract was contaminated at 1 µg/g (0.5 g tissue ml;
dilution factor, 1/30 for both samples). Plankton chromatogram is
qualitative only. Integrator attenuation was set at 8 for the mussel
sample and at 5 for the clam and plankton samples. (Reproduced
from ref. 225: J. AOAC Int., (1995) 78, p. 703, Fig. 9.).
Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins
Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) is a severe gastrointestinal illness caused by consumption of
shellfish contaminated with toxigenic dinoflagellates. The main toxins responsible for DSP are okadaic
acid (OA), dinophysistoxin-1 (DTX-1), DTX-2, and DTX-3 which are lipophilic polyether compounds.
HPLC with pre-column fluorescent derivatization in the presence of ADAM has been used in many
laboratories worldwide [226]. A representative new method for DSP toxins analysis on mussels
employs aqueous-methanolic extraction and partitioning into chloroform followed by SPE (NH ) clean-
2
up and derivatization with ADAM (Fig. 1.2.17) [227]. A problem with ADAM is its instability, which
leads to decomposition products that interfere in the analysis. To solve this problem, the method for in
situ formation of ADAM from the stable 9-anthraldehyde hydrazone has been used for the
derivatization of DSP toxins [228].
A silica or Florisil column clean-up after the ADAM reaction is necessary to eliminate decomposition
http://emedia.netlibrary.com/nlreader/nlreader.dll?bookid=17968&filename=Page_40.html 30/09/2003