Page 269 - Modern Optical Engineering The Design of Optical Systems
P. 269
Optical Coatings 249
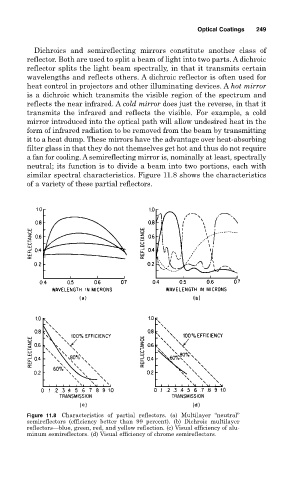
Dichroics and semireflecting mirrors constitute another class of
reflector. Both are used to split a beam of light into two parts. A dichroic
reflector splits the light beam spectrally, in that it transmits certain
wavelengths and reflects others. A dichroic reflector is often used for
heat control in projectors and other illuminating devices. A hot mirror
is a dichroic which transmits the visible region of the spectrum and
reflects the near infrared. A cold mirror does just the reverse, in that it
transmits the infrared and reflects the visible. For example, a cold
mirror introduced into the optical path will allow undesired heat in the
form of infrared radiation to be removed from the beam by transmitting
it to a heat dump. These mirrors have the advantage over heat-absorbing
filter glass in that they do not themselves get hot and thus do not require
a fan for cooling. A semireflecting mirror is, nominally at least, spectrally
neutral; its function is to divide a beam into two portions, each with
similar spectral characteristics. Figure 11.8 shows the characteristics
of a variety of these partial reflectors.
Figure 11.8 Characteristics of partial reflectors. (a) Multilayer “neutral”
semireflectors (efficiency better than 99 percent). (b) Dichroic multilayer
reflectors—blue, green, red, and yellow reflection. (c) Visual efficiency of alu-
minum semireflectors. (d) Visual efficiency of chrome semireflectors.