Page 39 - Modern physical chemistry
P. 39
28 Structure in Molecules and Atoms
f3
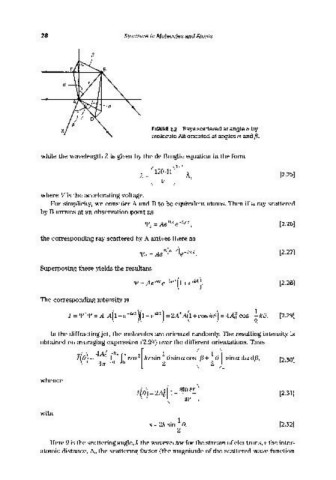
FIGURE 2.2 Rays scattered at angle e by
molecule AB oriented at angles a and [3.
while the wavelength A is given by the de Broglie equation in the form
A - 150.41 ( J A [2.25]
1I2
- V '
where V is the accelerating voltage.
For simplicity, we consider A and B to be equivalent atoms. Then if a ray scattered
by B arrives at an observation point as
[2.26]
the corresponding ray scattered by A arrives there as
[2.27]
Superposing these yields the resultant
'J' = Ae ika e -iw t (1 + e iko ). [2.28]
The corresponding intensity is
ik
1= 'J'*'J' = A*A(l+ e- O)(l+ e ikO ) = 2A*A(1 + cos kD) = 4A5 cos kkO. [2.29]
2
In the diffracting jet, the molecules are oriented randomly. The resulting intensity is
obtained on averaging expression (2.29) over the different orientations. Thus
i(o) = 4:; n: COS [ krSin~osmacoS[p+H}ma da dP, [2.30]
2
whence
[2.31]
with
s = 2ksin.!e. [2.32]
2
Here () is the scattering angle, k the wavevector for the stream of electrons, r the inter-
atomic distance, ~ the scattering factor (the magnitude of the scattered wave function