Page 246 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 246
240 Multidimensional Chromatography
problem to be solved is the separation of the tryglicerides from the most polar ana-
lytes while keeping the transfer volume small. In order to achieve this, van der Hoff
et al. (60) used a 1 mm i.d. LC silica column (3 m) to obtain transfer volumes of
100 l, containing all the analytes of interest, while maintaining the separation
between the most polar analytes and the fat matrix. They analysed a number of dif-
ferent organochlorine compounds (PCBs, the DDT group, HCB and the HCHs) at
concentration levels of sub- g/kg in milk fat, by using an on-line LC–GC (ECD)
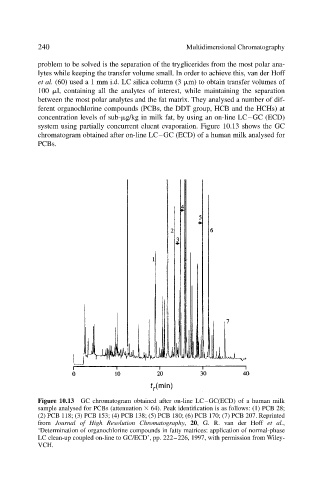
system using partially concurrent eluent evaporation. Figure 10.13 shows the GC
chromatogram obtained after on-line LC–GC (ECD) of a human milk analysed for
PCBs.
Figure 10.13 GC chromatogram obtained after on-line LC–GC(ECD) of a human milk
sample analysed for PCBs (attenuation 64). Peak identification is as follows: (1) PCB 28;
(2) PCB 118; (3) PCB 153; (4) PCB 138; (5) PCB 180; (6) PCB 170; (7) PCB 207. Reprinted
from Journal of High Resolution Chromatography, 20, G. R. van der Hoff et al.,
‘Determination of organochlorine compounds in fatty matrices: application of normal-phase
LC clean-up coupled on-line to GC/ECD’, pp. 222–226, 1997, with permission from Wiley-
VCH.