Page 353 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 353
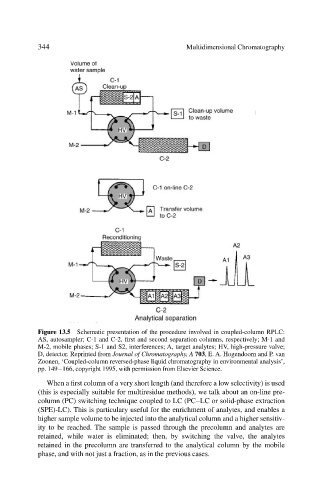
344 Multidimensional Chromatography
Figure 13.5 Schematic presentation of the procedure involved in coupled-column RPLC:
AS, autosampler; C-1 and C-2, first and second separation columns, respectively; M-1 and
M-2, mobile phases; S-1 and S2, interferences; A, target analytes; HV, high-pressure valve;
D, detector. Reprinted from Journal of Chromatography, A 703, E. A. Hogendoorn and P. van
Zoonen, ‘Coupled-column reversed-phase liquid chromatography in environmental analysis’,
pp. 149–166, copyright 1995, with permission from Elsevier Science.
When a first column of a very short length (and therefore a low selectivity) is used
(this is especially suitable for multiresidue methods), we talk about an on-line pre-
column (PC) switching technique coupled to LC (PC–LC or solid-phase extraction
(SPE)-LC). This is particulary useful for the enrichment of analytes, and enables a
higher sample volume to be injected into the analytical column and a higher sensitiv-
ity to be reached. The sample is passed through the precolumn and analytes are
retained, while water is eliminated; then, by switching the valve, the analytes
retained in the precolumn are transferred to the analytical column by the mobile
phase, and with not just a fraction, as in the previous cases.