Page 83 - Neural Network Modeling and Identification of Dynamical Systems
P. 83
2.3 DYNAMIC NEURAL NETWORK ADAPTATION METHODS 71
Strong pretuning is oriented to the adaptation
of the ANN model in a wide range of condi-
tions. A characteristic architectural feature of
the ANN model in this case is the presence of
NM elements in the processing elements, along
with the working elements, as well as insert ele-
ments affecting the parameters of the NM work-
ing elements. This approach allows implement-
ing both parametric and structural adaptation of
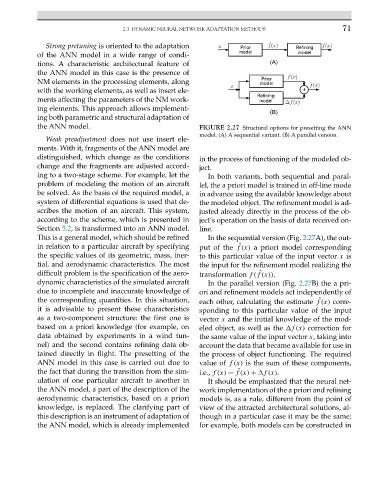
the ANN model. FIGURE 2.27 Structural options for presetting the ANN
model. (A) A sequential variant. (B) A parallel version.
Weak preadjustment does not use insert ele-
ments. With it, fragments of the ANN model are
distinguished, which change as the conditions in the process of functioning of the modeled ob-
change and the fragments are adjusted accord- ject.
ing to a two-stage scheme. For example, let the In both variants, both sequential and paral-
problem of modeling the motion of an aircraft lel, the a priori model is trained in off-line mode
be solved. As the basis of the required model, a in advance using the available knowledge about
system of differential equations is used that de- the modeled object. The refinement model is ad-
scribes the motion of an aircraft. This system, justed already directly in the process of the ob-
according to the scheme, which is presented in ject’s operation on the basis of data received on-
Section 5.2, is transformed into an ANN model. line.
This is a general model, which should be refined In the sequential version (Fig. 2.27A), the out-
in relation to a particular aircraft by specifying put of the f(x) a priori model corresponding
ˆ
the specific values of its geometric, mass, iner- to this particular value of the input vector x is
tial, and aerodynamic characteristics. The most the input for the refinement model realizing the
difficult problem is the specification of the aero- transformation f(f(x)).
ˆ
dynamic characteristics of the simulated aircraft In the parallel version (Fig. 2.27B) the a pri-
due to incomplete and inaccurate knowledge of ori and refinement models act independently of
the corresponding quantities. In this situation, each other, calculating the estimate f(x) corre-
ˆ
it is advisable to present these characteristics sponding to this particular value of the input
as a two-component structure: the first one is vector x and the initial knowledge of the mod-
based on a priori knowledge (for example, on eled object, as well as the f (x) correction for
data obtained by experiments in a wind tun- the same value of the input vector x, taking into
nel) and the second contains refining data ob- account the data that became available for use in
tained directly in flight. The presetting of the the process of object functioning. The required
ANN model in this case is carried out due to value of f(x) is the sum of these components,
the fact that during the transition from the sim- i.e., f(x) = f(x) + f (x).
ˆ
ulation of one particular aircraft to another in It should be emphasized that the neural net-
the ANN model, a part of the description of the work implementation of the a priori and refining
aerodynamic characteristics, based on a priori models is, as a rule, different from the point of
knowledge, is replaced. The clarifying part of view of the attracted architectural solutions, al-
this description is an instrument of adaptation of though in a particular case it may be the same;
the ANN model, which is already implemented for example, both models can be constructed in