Page 433 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 433
386 New Trends in Eco-efficient and Recycled Concrete
blast furnace slag yielded appropriate binding characteristics (Arullrajah et al.,
2016). Crushed bricks and RA concrete (RAC) were geopolymer stabilised and the
systems could be used for pavement base/sub-base applications. CCR was also used
for stabilising water treatment sludge by means the alkali activation with NaOH/
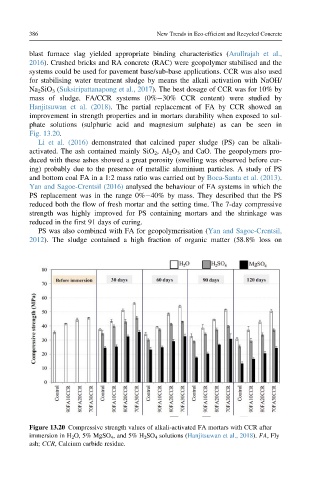
Na 2 SiO 3 (Suksiripattanapong et al., 2017). The best dosage of CCR was for 10% by
mass of sludge. FA/CCR systems (0% 30% CCR content) were studied by
Hanjitsuwan et al. (2018). The partial replacement of FA by CCR showed an
improvement in strength properties and in mortars durability when exposed to sul-
phate solutions (sulphuric acid and magnesium sulphate) as can be seen in
Fig. 13.20.
Li et al. (2016) demonstrated that calcined paper sludge (PS) can be alkali-
activated. The ash contained mainly SiO 2 ,Al 2 O 3 and CaO. The geopolymers pro-
duced with these ashes showed a great porosity (swelling was observed before cur-
ing) probably due to the presence of metallic aluminium particles. A study of PS
and bottom coal FA in a 1:2 mass ratio was carried out by Boca-Santa et al. (2013).
Yan and Sagoe-Crentsil (2016) analysed the behaviour of FA systems in which the
PS replacement was in the range 0% 40% by mass. They described that the PS
reduced both the flow of fresh mortar and the setting time. The 7-day compressive
strength was highly improved for PS containing mortars and the shrinkage was
reduced in the first 91 days of curing.
PS was also combined with FA for geopolymerisation (Yan and Sagoe-Crentsil,
2012). The sludge contained a high fraction of organic matter (58.8% loss on
Figure 13.20 Compressive strength values of alkali-activated FA mortars with CCR after
immersion in H 2 O, 5% MgSO 4 , and 5% H 2 SO 4 solutions (Hanjitsuwan et al., 2018). FA, Fly
ash; CCR, Calcium carbide residue.