Page 437 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 437
Application of alkali-activated industrial waste 389
after curing at 35 C. Increasing curing temperature at 60 C raises the strength to
close 50 MPa, however, at 20 and 90 C strong decreasing was detected. Detphan
and Chindaprasirt (2009) determined the density and strength of the geopolymer
mortars with RHA/FA mass ratios of 0/100, 20/80, 40/60, and 60/40 and Hwang
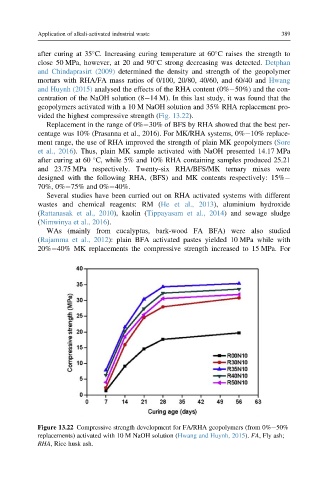
and Huynh (2015) analysed the effects of the RHA content (0% 50%) and the con-
centration of the NaOH solution (8 14 M). In this last study, it was found that the
geopolymers activated with a 10 M NaOH solution and 35% RHA replacement pro-
vided the highest compressive strength (Fig. 13.22).
Replacement in the range of 0% 30% of BFS by RHA showed that the best per-
centage was 10% (Prasanna et al., 2016). For MK/RHA systems, 0% 10% replace-
ment range, the use of RHA improved the strength of plain MK geopolymers (Sore
et al., 2016). Thus, plain MK sample activated with NaOH presented 14.17 MPa
after curing at 60 C, while 5% and 10% RHA containing samples produced 25.21
and 23.75 MPa respectively. Twenty-six RHA/BFS/MK ternary mixes were
designed with the following RHA, (BFS) and MK contents respectively: 15%
70%, 0% 75% and 0% 40%.
Several studies have been carried out on RHA activated systems with different
wastes and chemical reagents: RM (He et al., 2013), aluminium hydroxide
(Rattanasak et al., 2010), kaolin (Tippayasam et al., 2014) and sewage sludge
(Nimwinya et al., 2016).
WAs (mainly from eucalyptus, bark-wood FA BFA) were also studied
(Rajamma et al., 2012): plain BFA activated pastes yielded 10 MPa while with
20% 40% MK replacements the compressive strength increased to 15 MPa. For
Figure 13.22 Compressive strength development for FA/RHA geopolymers (from 0% 50%
replacements) activated with 10 M NaOH solution (Hwang and Huynh, 2015). FA, Fly ash;
RHA, Rice husk ash.