Page 439 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 439
Application of alkali-activated industrial waste 391
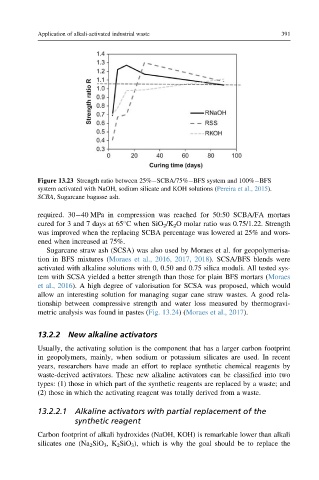
Figure 13.23 Strength ratio between 25% SCBA/75% BFS system and 100% BFS
system activated with NaOH, sodium silicate and KOH solutions (Pereira et al., 2015).
SCBA, Sugarcane bagasse ash.
required. 30 40 MPa in compression was reached for 50:50 SCBA/FA mortars
cured for 3 and 7 days at 65 C when SiO 2 /K 2 O molar ratio was 0.75/1.22. Strength
was improved when the replacing SCBA percentage was lowered at 25% and wors-
ened when increased at 75%.
Sugarcane straw ash (SCSA) was also used by Moraes et al. for geopolymerisa-
tion in BFS mixtures (Moraes et al., 2016, 2017, 2018). SCSA/BFS blends were
activated with alkaline solutions with 0, 0.50 and 0.75 silica moduli. All tested sys-
tem with SCSA yielded a better strength than those for plain BFS mortars (Moraes
et al., 2016). A high degree of valorisation for SCSA was proposed, which would
allow an interesting solution for managing sugar cane straw wastes. A good rela-
tionship between compressive strength and water loss measured by thermogravi-
metric analysis was found in pastes (Fig. 13.24)(Moraes et al., 2017).
13.2.2 New alkaline activators
Usually, the activating solution is the component that has a larger carbon footprint
in geopolymers, mainly, when sodium or potassium silicates are used. In recent
years, researchers have made an effort to replace synthetic chemical reagents by
waste-derived activators. These new alkaline activators can be classified into two
types: (1) those in which part of the synthetic reagents are replaced by a waste; and
(2) those in which the activating reagent was totally derived from a waste.
13.2.2.1 Alkaline activators with partial replacement of the
synthetic reagent
Carbon footprint of alkali hydroxides (NaOH, KOH) is remarkable lower than alkali
silicates one (Na 2 SiO 3 ,K 2 SiO 3 ), which is why the goal should be to replace the