Page 125 - Numerical Analysis and Modelling in Geomechanics
P. 125
106 C.W.W.NG AND Q.SHI
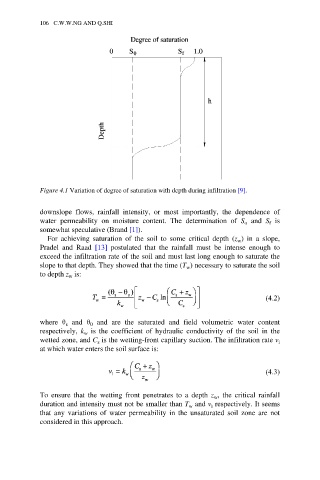
Figure 4.1 Variation of degree of saturation with depth during infiltration [9].
downslope flows, rainfall intensity, or most importantly, the dependence of
water permeability on moisture content. The determination of S o and S f is
somewhat speculative (Brand [1]).
For achieving saturation of the soil to some critical depth (z ) in a slope,
w
Pradel and Raad [13] postulated that the rainfall must be intense enough to
exceed the infiltration rate of the soil and must last long enough to saturate the
slope to that depth. They showed that the time (T ) necessary to saturate the soil
w
to depth z is:
w
(4.2)
where θ s and θ 0 and are the saturated and field volumetric water content
respectively, k w is the coefficient of hydraulic conductivity of the soil in the
wetted zone, and C is the wetting-front capillary suction. The infiltration rate v i
s
at which water enters the soil surface is:
(4.3)
To ensure that the wetting front penetrates to a depth z , the critical rainfall
w
duration and intensity must not be smaller than T and v respectively. It seems
w
i
that any variations of water permeability in the unsaturated soil zone are not
considered in this approach.