Page 254 - Numerical Analysis and Modelling in Geomechanics
P. 254
F.PERGALANI, V.PETRINI, A.PUGLIESE AND T.SANÒ 235
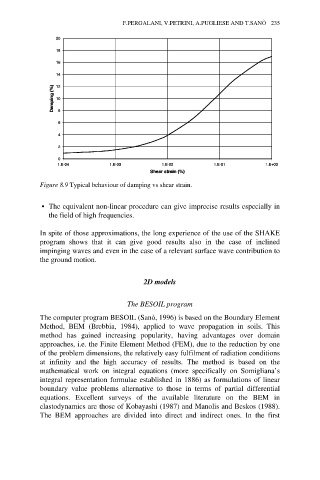
Figure 8.9 Typical behaviour of damping vs shear strain.
• The equivalent non-linear procedure can give imprecise results especially in
the field of high frequencies.
In spite of those approximations, the long experience of the use of the SHAKE
program shows that it can give good results also in the case of inclined
impinging waves and even in the case of a relevant surface wave contribution to
the ground motion.
2D models
The BESOIL program
The computer program BESOIL (Sanò, 1996) is based on the Boundary Element
Method, BEM (Brebbia, 1984), applied to wave propagation in soils. This
method has gained increasing popularity, having advantages over domain
approaches, i.e. the Finite Element Method (FEM), due to the reduction by one
of the problem dimensions, the relatively easy fulfilment of radiation conditions
at infinity and the high accuracy of results. The method is based on the
mathematical work on integral equations (more specifically on Somigliana’s
integral representation formulae established in 1886) as formulations of linear
boundary value problems alternative to those in terms of partial differential
equations. Excellent surveys of the available literature on the BEM in
elastodynamics are those of Kobayashi (1987) and Manolis and Beskos (1988).
The BEM approaches are divided into direct and indirect ones. In the first