Page 288 - Offshore Electrical Engineering Manual
P. 288
Percentage Distortion Definition 275
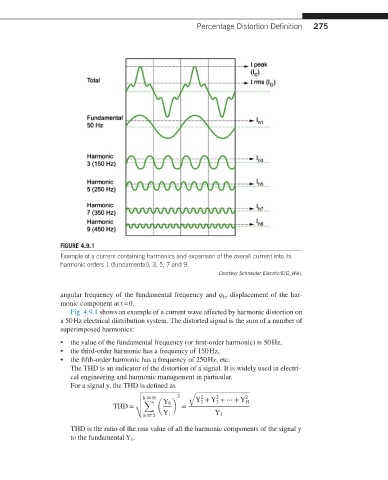
FIGURE 4.9.1
Example of a current containing harmonics and expansion of the overall current into its
harmonic orders 1 (fundamental), 3, 5, 7 and 9.
Courtesy Schneider Electric/EIG_Wiki.
angular frequency of the fundamental frequency and φ , displacement of the har-
h
monic component at t = 0.
Fig. 4.9.1 shows an example of a current wave affected by harmonic distortion on
a 50 Hz electrical distribution system. The distorted signal is the sum of a number of
superimposed harmonics:
• the value of the fundamental frequency (or first-order harmonic) is 50 Hz,
• the third-order harmonic has a frequency of 150 Hz,
• the fifth-order harmonic has a frequency of 250 Hz, etc.
The THD is an indicator of the distortion of a signal. It is widely used in electri-
cal engineering and harmonic management in particular.
For a signal y, the THD is defined as
� √
� ) 2 2 2 2
� h= H ( Y h Y + Y +⋯ + Y H
3
2
∑
THD = � =
h= 2 Y 1 Y 1
THD is the ratio of the rms value of all the harmonic components of the signal y
to the fundamental Y .
1