Page 21 - Oil and Gas Production Handbook An Introduction to Oil and Gas Production
P. 21
3 Reservoir and wellheads
There are three main types of conventional wells. The most common is an oil
well with associated gas. Natural gas wells are drilled specifically for natural
gas, and contain little or no oil. Condensate wells contain natural gas, as well
as a liquid condensate. This condensate is a liquid hydrocarbon mixture that
is often separated from the natural gas either at the wellhead, or during the
processing of the natural gas. Depending on the type of well that is being
drilled, completion may differ slightly. It is important to remember that natural
gas, being lighter than air, will naturally rise to the surface of a well.
Consequently, lifting equipment and well treatment are not necessary in
many natural gas and condensate wells, while for oil wells many types of
artificial lift might be installed, particularly as the reservoir pressure falls
during years of production.
3.1 Crude oil and natural gas
3.1.1 Crude oil
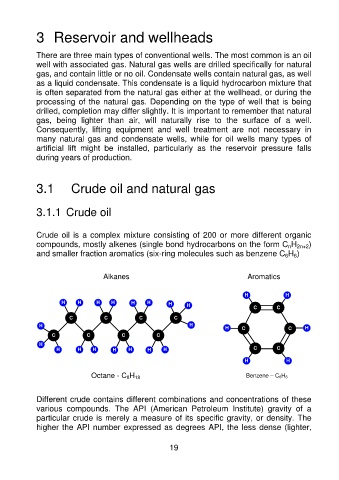
Crude oil is a complex mixture consisting of 200 or more different organic
compounds, mostly alkenes (single bond hydrocarbons on the form C nH 2n+2)
and smaller fraction aromatics (six-ring molecules such as benzene C 6H 6)
Alkanes Aromatics
H H
H H H H H H H H C C
C C C C
H H H C C H
C C C C
H
H H H H H H H C C
H H
Octane - C 8H 18 Benzene – C 6H 6
Different crude contains different combinations and concentrations of these
various compounds. The API (American Petroleum Institute) gravity of a
particular crude is merely a measure of its specific gravity, or density. The
higher the API number expressed as degrees API, the less dense (lighter,
19