Page 27 - Oil and Gas Production Handbook An Introduction to Oil and Gas Production
P. 27
As the well is sunk into the ground, the weight of the drill string increases
and might reach 500 metric tons or more for a 3000 meter deep well. The
drawwork and top drive must be precisely controlled so as not to overload
and break the drill string or the cone. Typical values are 50kN force on the
bit and a torque of 1-1.5 kNm at 40-80 RPM for an 8 inch cone. ROP (Rate
of Penetration) is very dependant on depth and could be as much as 20
meters per hour for shallow sandstone and dolomite (chalk) and as low as 1
m/hour on deep shale rock and granite.
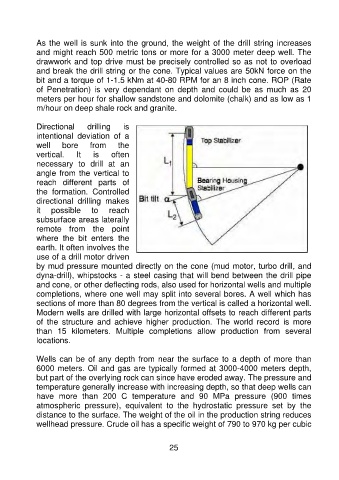
Directional drilling is
intentional deviation of a
well bore from the
vertical. It is often
necessary to drill at an
angle from the vertical to
reach different parts of
the formation. Controlled
directional drilling makes
it possible to reach
subsurface areas laterally
remote from the point
where the bit enters the
earth. It often involves the
use of a drill motor driven
by mud pressure mounted directly on the cone (mud motor, turbo drill, and
dyna-drill), whipstocks - a steel casing that will bend between the drill pipe
and cone, or other deflecting rods, also used for horizontal wells and multiple
completions, where one well may split into several bores. A well which has
sections of more than 80 degrees from the vertical is called a horizontal well.
Modern wells are drilled with large horizontal offsets to reach different parts
of the structure and achieve higher production. The world record is more
than 15 kilometers. Multiple completions allow production from several
locations.
Wells can be of any depth from near the surface to a depth of more than
6000 meters. Oil and gas are typically formed at 3000-4000 meters depth,
but part of the overlying rock can since have eroded away. The pressure and
temperature generally increase with increasing depth, so that deep wells can
have more than 200 C temperature and 90 MPa pressure (900 times
atmospheric pressure), equivalent to the hydrostatic pressure set by the
distance to the surface. The weight of the oil in the production string reduces
wellhead pressure. Crude oil has a specific weight of 790 to 970 kg per cubic
25