Page 106 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 106
Light Sources and Transmitters
96 Chapter Six
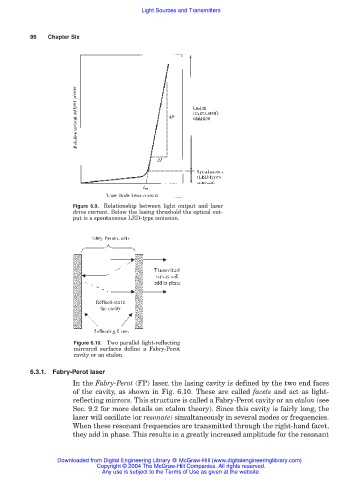
Figure 6.9. Relationship between light output and laser
drive current. Below the lasing threshold the optical out-
put is a spontaneous LED-type emission.
Figure 6.10. Two parallel light-reflecting
mirrored surfaces define a Fabry-Perot
cavity or an etalon.
6.3.1. Fabry-Perot laser
In the Fabry-Perot (FP) laser, the lasing cavity is defined by the two end faces
of the cavity, as shown in Fig. 6.10. These are called facets and act as light-
reflecting mirrors. This structure is called a Fabry-Perot cavity or an etalon (see
Sec. 9.2 for more details on etalon theory). Since this cavity is fairly long, the
laser will oscillate (or resonate) simultaneously in several modes or frequencies.
When these resonant frequencies are transmitted through the right-hand facet,
they add in phase. This results in a greatly increased amplitude for the resonant
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.