Page 295 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 295
Optical Networks
Optical Networks 285
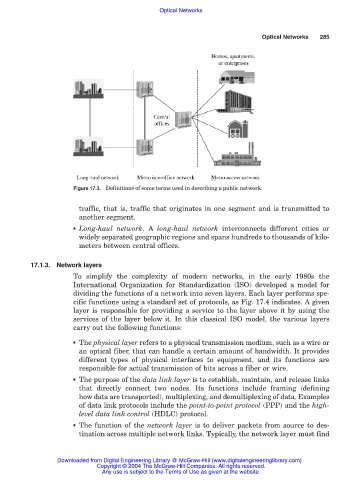
Figure 17.3. Definitions of some terms used in describing a public network.
traffic, that is, traffic that originates in one segment and is transmitted to
another segment.
■ Long-haul network. A long-haul network interconnects different cities or
widely separated geographic regions and spans hundreds to thousands of kilo-
meters between central offices.
17.1.3. Network layers
To simplify the complexity of modern networks, in the early 1980s the
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) developed a model for
dividing the functions of a network into seven layers. Each layer performs spe-
cific functions using a standard set of protocols, as Fig. 17.4 indicates. A given
layer is responsible for providing a service to the layer above it by using the
services of the layer below it. In this classical ISO model, the various layers
carry out the following functions:
■ The physical layer refers to a physical transmission medium, such as a wire or
an optical fiber, that can handle a certain amount of bandwidth. It provides
different types of physical interfaces to equipment, and its functions are
responsible for actual transmission of bits across a fiber or wire.
■ The purpose of the data link layer is to establish, maintain, and release links
that directly connect two nodes. Its functions include framing (defining
how data are transported), multiplexing, and demultiplexing of data. Examples
of data link protocols include the point-to-point protocol (PPP) and the high-
level data link control (HDLC) protocol.
■ The function of the network layer is to deliver packets from source to des-
tination across multiple network links. Typically, the network layer must find
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.