Page 298 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 298
Optical Networks
288 Chapter Seventeen
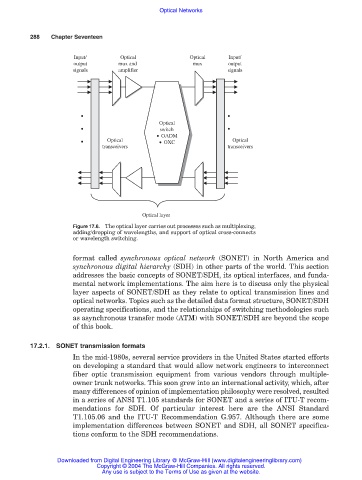
Input/ Optical Optical Input/
output mux and mux output
signals amplifier signals
• •
Optical
Optical
• switch •
Switch
• OADM
• OADM
• Optical • OXC Optical
transceivers OXC transceivers
Optical layer
Figure 17.6. The optical layer carries out processes such as multiplexing,
adding/dropping of wavelengths, and support of optical cross-connects
or wavelength switching.
format called synchronous optical network (SONET) in North America and
synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) in other parts of the world. This section
addresses the basic concepts of SONET/SDH, its optical interfaces, and funda-
mental network implementations. The aim here is to discuss only the physical
layer aspects of SONET/SDH as they relate to optical transmission lines and
optical networks. Topics such as the detailed data format structure, SONET/SDH
operating specifications, and the relationships of switching methodologies such
as asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) with SONET/SDH are beyond the scope
of this book.
17.2.1. SONET transmission formats
In the mid-1980s, several service providers in the United States started efforts
on developing a standard that would allow network engineers to interconnect
fiber optic transmission equipment from various vendors through multiple-
owner trunk networks. This soon grew into an international activity, which, after
many differences of opinion of implementation philosophy were resolved, resulted
in a series of ANSI T1.105 standards for SONET and a series of ITU-T recom-
mendations for SDH. Of particular interest here are the ANSI Standard
T1.105.06 and the ITU-T Recommendation G.957. Although there are some
implementation differences between SONET and SDH, all SONET specifica-
tions conform to the SDH recommendations.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.