Page 206 - Optical Switching And Networking Handbook
P. 206
09_200023_CH08/Batesx 1/17/01 8:20 AM Page 191
High-Speed Applications 191
its simplest form, two devices are connected with an optical fiber
(with any repeaters as necessary) as a point-to-point circuit. As the
entry-level point into SONET/SDH architecture, the inputs and out-
puts are identical. In this environment, the network can act as a
stand-alone environment and not have to interface with the public
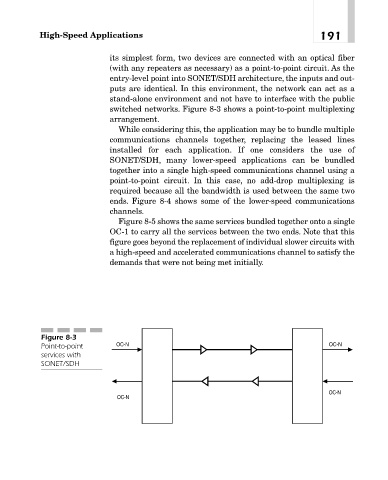
switched networks. Figure 8-3 shows a point-to-point multiplexing
arrangement.
While considering this, the application may be to bundle multiple
communications channels together, replacing the leased lines
installed for each application. If one considers the use of
SONET/SDH, many lower-speed applications can be bundled
together into a single high-speed communications channel using a
point-to-point circuit. In this case, no add-drop multiplexing is
required because all the bandwidth is used between the same two
ends. Figure 8-4 shows some of the lower-speed communications
channels.
Figure 8-5 shows the same services bundled together onto a single
OC-1 to carry all the services between the two ends. Note that this
figure goes beyond the replacement of individual slower circuits with
a high-speed and accelerated communications channel to satisfy the
demands that were not being met initially.
Figure 8-3
Point-to-point OC-N OC-N
services with
SONET/SDH
OC-N
OC-N