Page 226 - Optical Switching And Networking Handbook
P. 226
09_200023_CH08/Batesx 1/17/01 8:20 AM Page 211
High-Speed Applications 211
The Wide-Area Network
When provisioning for the long-haul networks, the carriers have to
take into account that they will interface with local providers, that is,
unless they become the local provider too. However the interconnec-
tion is made, the wide area is where most of the infrastructure was
built in the past because of the economics of providing the fiber-
based (SONET/SDH) networks to carry long-distance traffic and
consolidated data communications. This worked, but as seen, the
new battlefront is at the metropolitan area. Thus, when the commu-
nications providers use their interconnectivity, they must take into
account how they will link the metropolitan and wide areas together.
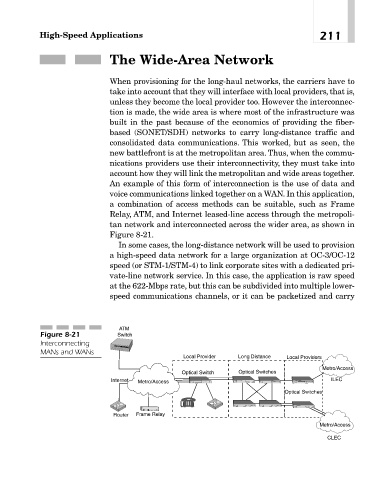
An example of this form of interconnection is the use of data and
voice communications linked together on a WAN. In this application,
a combination of access methods can be suitable, such as Frame
Relay, ATM, and Internet leased-line access through the metropoli-
tan network and interconnected across the wider area, as shown in
Figure 8-21.
In some cases, the long-distance network will be used to provision
a high-speed data network for a large organization at OC-3/OC-12
speed (or STM-1/STM-4) to link corporate sites with a dedicated pri-
vate-line network service. In this case, the application is raw speed
at the 622-Mbps rate, but this can be subdivided into multiple lower-
speed communications channels, or it can be packetized and carry
ATM
Figure 8-21 Switch
Interconnecting
MANs and WANs
Local Provider Long Distance Local Providers
Metro/Access
Optical Switch Optical Switches
Internet Metro/Access ILEC
Optical Switches
Router Frame Relay
Metro/Access
CLEC