Page 48 - Optical Switching And Networking Handbook
P. 48
03_200023_CH02/Batesx 1/17/01 8:17 AM Page 33
Basic Fiberoptics Technologies 33
usage, the cost issues are far less critical. For years now, carriers
have chosen to install fiber whenever possible in their backbone.The
issue they faced was which type of fiber to use: single mode or mul-
timode. They have pretty well settled on single mode in all new
installations.
The Fiber Concept
It is important for nonengineering professionals to understand the
basics of fiberoptics and the use of multiplexing. However, it is not
the intent of this book to make the reader an engineering wizard.
Nevertheless, some technically simplified concepts are required to
“talk the talk.” First, it is necessary to understand the basic compo-
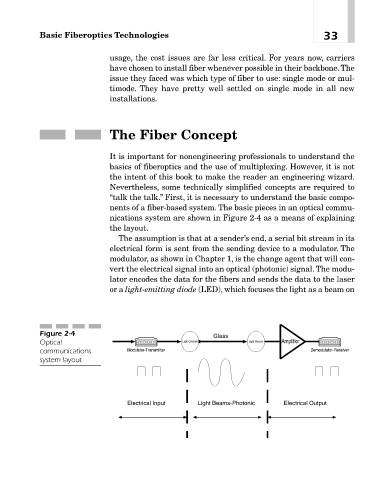
nents of a fiber-based system. The basic pieces in an optical commu-
nications system are shown in Figure 2-4 as a means of explaining
the layout.
The assumption is that at a sender’s end, a serial bit stream in its
electrical form is sent from the sending device to a modulator. The
modulator, as shown in Chapter 1, is the change agent that will con-
vert the electrical signal into an optical (photonic) signal. The modu-
lator encodes the data for the fibers and sends the data to the laser
or a light-emitting diode (LED), which focuses the light as a beam on
Figure 2-4 Glass
Optical Light Created Light Sensor Amplifier
communications Modulator-Transmitter Demodulator-Receiver
system layout
Electrical Input Light Beams-Photonic Electrical Output