Page 87 - Optical Switching And Networking Handbook
P. 87
04_200023_CH03/Batesx 1/17/01 9:42 AM Page 72
72 Chapter 3
Multiplexing lower-order signals to higher-order signals
Stuffing of bits necessary to handle the various lower-speed
asynchronous channels and filling up the spare bits to keep
everything in alignment.
The SONET equipment provides these functions. SONET can
carry very large payloads, as we have seen in the hierarchy of the
data speeds. Up to now, we have seen the primary mapping and lay-
out of an STS-1 (OC-1). SONET equipment can add the value neces-
sary to protect investments by either lower- or higher-rate
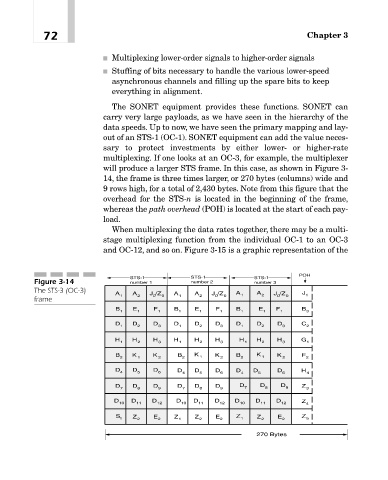
multiplexing. If one looks at an OC-3, for example, the multiplexer
will produce a larger STS frame. In this case, as shown in Figure 3-
14, the frame is three times larger, or 270 bytes (columns) wide and
9 rows high, for a total of 2,430 bytes. Note from this figure that the
overhead for the STS-n is located in the beginning of the frame,
whereas the path overhead (POH) is located at the start of each pay-
load.
When multiplexing the data rates together, there may be a multi-
stage multiplexing function from the individual OC-1 to an OC-3
and OC-12, and so on. Figure 3-15 is a graphic representation of the
POH
STS-1 STS-1 STS-1
Figure 3-14 number 1 number 2 number 3
The STS-3 (OC-3)
A 1 A 2 J /Z 0 A 1 A 2 J /Z 0 A 1 A 2 J /Z 0 J 1
0
0
0
frame
B E F B E F B E F B
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3
D D D D D D D D D C
1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 2
H H H H H H H H H G
1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1
B K K B K K B K K F
2 1 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 2
D D D D D D D D D H
4 5 6 4 5 6 4 5 6 4
D D D D D D D D D Z
7 8 9 7 8 9 7 8 9 3
D D D D D D D D D Z
10 11 12 10 11 12 10 11 12 4
S Z E Z Z E Z Z E Z
1 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 5
270 Bytes