Page 275 - Optofluidics Fundamentals, Devices, and Applications
P. 275
Optofluidic Dye Lasers 249
Sample Spectrometer
Pump
LCORR
WGM
Gain
medium
Tunable laser Detector WGM
Fiber taper Fiber taper Camera
(a) (b)
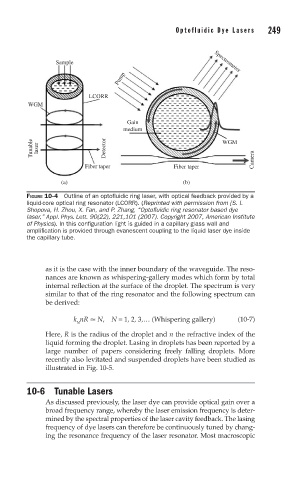
FIGURE 10-4 Outline of an optofluidic ring laser, with optical feedback provided by a
liquid-core optical ring resonator (LCORR). (Reprinted with permission from [S. I.
Shopova, H. Zhou, X. Fan, and P. Zhang, “Optofluidic ring resonator based dye
laser,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(22), 221,101 (2007). Copyright 2007, American Institute
of Physics). In this configuration light is guided in a capillary glass wall and
amplification is provided through evanescent coupling to the liquid laser dye inside
the capillary tube.
as it is the case with the inner boundary of the waveguide. The reso-
nances are known as whispering-gallery modes which form by total
internal reflection at the surface of the droplet. The spectrum is very
similar to that of the ring resonator and the following spectrum can
be derived:
k nR N, N = 1, 2, 3,… (Whispering gallery) (10-7)
N
Here, R is the radius of the droplet and n the refractive index of the
liquid forming the droplet. Lasing in droplets has been reported by a
large number of papers considering freely falling droplets. More
recently also levitated and suspended droplets have been studied as
illustrated in Fig. 10-5.
10-6 Tunable Lasers
As discussed previously, the laser dye can provide optical gain over a
broad frequency range, whereby the laser emission frequency is deter-
mined by the spectral properties of the laser cavity feedback. The lasing
frequency of dye lasers can therefore be continuously tuned by chang-
ing the resonance frequency of the laser resonator. Most macroscopic