Page 224 - Origin and Prediction of Abnormal Formation Pressures
P. 224
TECTONICS AND OVERPRESSURED FORMATIONS 199
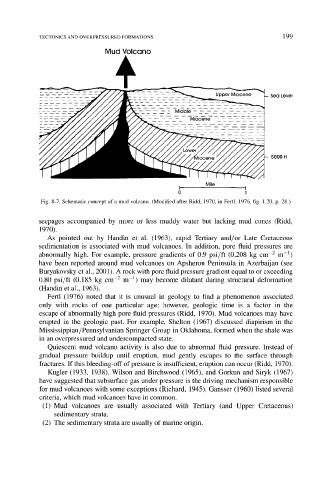
Mud Volcano
Ill
Upper Miocene Sea Level
Middle
Miocene
5000 ft
Mile
! t
0 1
Fig. 8-7. Schematic concept of a mud volcano. (Modified after Ridd, 1970, in Fertl, 1976, fig. 1.20, p. 28.)
seepages accompanied by more or less muddy water but lacking mud cones (Ridd,
1970).
As pointed out by Handin et al. (1963), rapid Tertiary and/or Late Cretaceous
sedimentation is associated with mud volcanoes. In addition, pore fluid pressures are
abnormally high. For example, pressure gradients of 0.9 psi/ft (0.208 kg cm -2 m -1)
have been reported around mud volcanoes on Apsheron Peninsula in Azerbaijan (see
Buryakovsky et al., 2001). A rock with pore fluid pressure gradient equal to or exceeding
0.80 psi/ft (0.185 kg cm -2 m -1) may become dilatant during structural deformation
(Handin et al., 1963).
Fertl (1976) noted that it is unusual in geology to find a phenomenon associated
only with rocks of one particular age; however, geologic time is a factor in the
escape of abnormally high pore fluid pressures (Ridd, 1970). Mud volcanoes may have
erupted in the geologic past. For example, Shelton (1967) discussed diapirism in the
Mississippian/Pennsylvanian Springer Group in Oklahoma, formed when the shale was
in an overpressured and undercompacted state.
Quiescent mud volcano activity is also due to abnormal fluid pressure. Instead of
gradual pressure buildup until eruption, mud gently escapes to the surface through
fractures. If this bleeding-off of pressure is insufficient, eruption can occur (Ridd, 1970).
Kugler (1933, 1938), Wilson and Birchwood (1965), and Gorkun and Siryk (1967)
have suggested that subsurface gas under pressure is the driving mechanism responsible
for mud volcanoes with some exceptions (Richard, 1945). Gansser (1960) listed several
criteria, which mud volcanoes have in common.
(1) Mud volcanoes are usually associated with Tertiary (and Upper Cretaceous)
sedimentary strata.
(2) The sedimentary strata are usually of marine origin.