Page 28 - PVT Property Correlations
P. 28
Introduction Chapter | 1 9
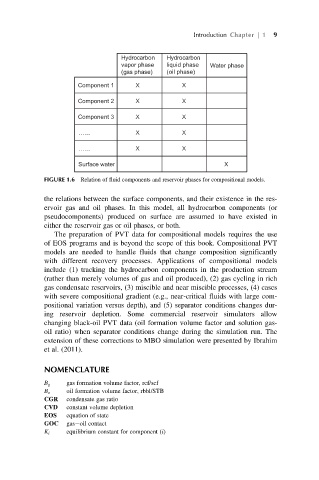
Hydrocarbon Hydrocarbon
vapor phase liquid phase Water phase
(gas phase) (oil phase)
Component 1 X X
Component 2 X X
Component 3 X X
…… X X
…… X X
Surface water X
FIGURE 1.6 Relation of fluid components and reservoir phases for compositional models.
the relations between the surface components, and their existence in the res-
ervoir gas and oil phases. In this model, all hydrocarbon components (or
pseudocomponents) produced on surface are assumed to have existed in
either the reservoir gas or oil phases, or both.
The preparation of PVT data for compositional models requires the use
of EOS programs and is beyond the scope of this book. Compositional PVT
models are needed to handle fluids that change composition significantly
with different recovery processes. Applications of compositional models
include (1) tracking the hydrocarbon components in the production stream
(rather than merely volumes of gas and oil produced), (2) gas cycling in rich
gas condensate reservoirs, (3) miscible and near miscible processes, (4) cases
with severe compositional gradient (e.g., near-critical fluids with large com-
positional variation versus depth), and (5) separator conditions changes dur-
ing reservoir depletion. Some commercial reservoir simulators allow
changing black-oil PVT data (oil formation volume factor and solution gas-
oil ratio) when separator conditions change during the simulation run. The
extension of these corrections to MBO simulation were presented by Ibrahim
et al. (2011).
NOMENCLATURE
B g gas formation volume factor, rcf/scf
B o oil formation volume factor, rbbl/STB
CGR condensate gas ratio
CVD constant volume depletion
EOS equation of state
GOC gas oil contact
equilibrium constant for component (i)
K i