Page 92 - PVT Property Correlations
P. 92
70 PVT Property Correlations
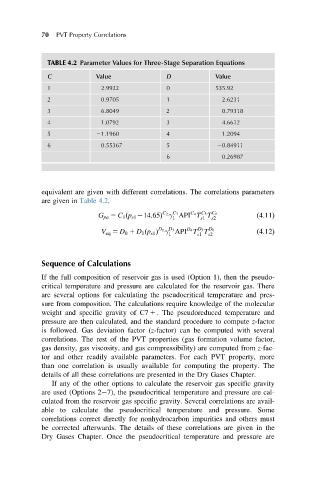
TABLE 4.2 Parameter Values for Three-Stage Separation Equations
Value Value
C D
1 2.9922 0 535.92
2 0.9705 1 2.6231
3 6.8049 2 0.79318
4 1.0792 3 4.6612
5 21.1960 4 1.2094
6 0.55367 5 20.84911
6 0.26987
equivalent are given with different correlations. The correlations parameters
are given in Table 4.2.
C 5
C 2 C 3
C 4
G pa 5 C 1 p s1 214:65ð Þ γ API T T C 6 ð4:11Þ
1 s1 s2
D 5
D 2 D 3
D 4
V eq 5 D 0 1 D 1 p s1 Þ γ API T T D 6 ð4:12Þ
ð
1 s1 s2
Sequence of Calculations
If the full composition of reservoir gas is used (Option 1), then the pseudo-
critical temperature and pressure are calculated for the reservoir gas. There
are several options for calculating the pseudocritical temperature and pres-
sure from composition. The calculations require knowledge of the molecular
weight and specific gravity of C7 1 . The pseudoreduced temperature and
pressure are then calculated, and the standard procedure to compute z-factor
is followed. Gas deviation factor (z-factor) can be computed with several
correlations. The rest of the PVT properties (gas formation volume factor,
gas density, gas viscosity, and gas compressibility) are computed from z-fac-
tor and other readily available parameters. For each PVT property, more
than one correlation is usually available for computing the property. The
details of all these correlations are presented in the Dry Gases Chapter.
If any of the other options to calculate the reservoir gas specific gravity
are used (Options 2 7), the pseudocritical temperature and pressure are cal-
culated from the reservoir gas specific gravity. Several correlations are avail-
able to calculate the pseudocritical temperature and pressure. Some
correlations correct directly for nonhydrocarbon impurities and others must
be corrected afterwards. The details of these correlations are given in the
Dry Gases Chapter. Once the pseudocritical temperature and pressure are