Page 11 - Packed bed columns for absorption, desorption, rectification and direct heat transfer
P. 11
drop is connected directly not with the gas velocity, but with its relative value
equal to the gas velocity w» only in case of dry packing, In case of irrigated
packing, it is the algebraic sum of the gas velocity and the liquid velocity at the
contact surface with the gas phase. That is why there is a difference in the
influence of the liquid phase on the gas hydrodynamics for co-current and
countercurrent flow. Because usually the gas velocity is many times greater than
the liquid one, in many cases the second effect can be neglected.
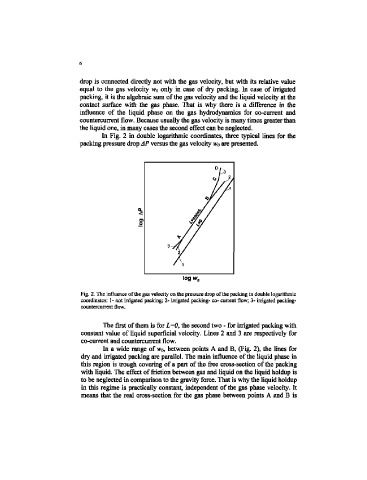
In Fig. 2 in double logarithmic coordinates, three typical lines for the
packing pressure drop AP versus the gas velocity Wo are presented.
logw.
Fig. 2, The influence of the gas velocity on the pressure drop of the packing in double logarithmic
coordinates: 1- not irrigated packing; 2- irrigated packing- co- current flow; 3- irrigated packing-
countereurrent flow.
The first of them is for L=0, the second two - for irrigated packing with
constant value of liquid superficial velocity. Lines 2 and 3 are respectively for
co-current and countercurrent flow.
In a wide range of w 0, between points A and B, (Fig. 2), the lines for
dry and irrigated packing are parallel. The main influence of the liquid phase in
this region is trough covering of a part of the free cross-section of the packing
with liquid. The effect of friction between gas and liquid on the liquid holdup is
to be neglected in comparison to the gravity force. That is why the liquid holdup
in this regime is practically constant, independent of the gas phase velocity. It
means that the real cross-section for the gas phase between points A and B is