Page 44 - Packed bed columns for absorption, desorption, rectification and direct heat transfer
P. 44
39
PA
Y A=- (123)
PB+PA •PB(*-XA l-(a-l)X A
where a } = — is called relative volatility.
PB
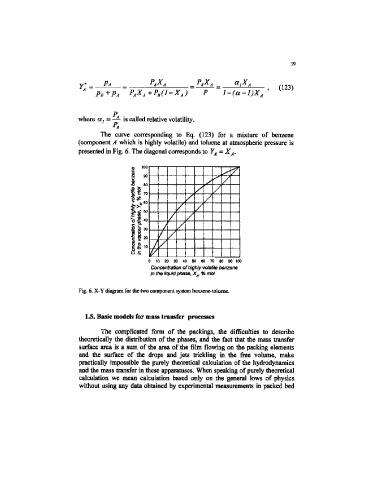
The curve corresponding to Eq. (123) for a mixture of benzene
(component A which is highly volatile) and toluene at atmospheric pressure is
presented in Fig. 6. The diagonal corresponds to Y A = X A.
® 100
I 90 y /
/ /
5 80 / /
: 70 /
/
1| 30 / /
/
II / A
10 /
•S
0 10 20 30 40 SO 60 70 80 90 100
Concentration of highly volatile benzene
in the liquid phase, X,, % mol
Fig, 6. X-Y diagram for the two component system benzene-toluene.
1.5. Basic models for mass transfer processes
The complicated form of the packings, the difficulties to describe
theoretically the distribution of the phases, and the fact that the mass transfer
surface area is a sum of the area of the film flowing on the packing elements
and the surface of the drops and jets trickling in the free volume, make
practically impossible the purely theoretical calculation of the hydrodynamics
and the mass transfer in these apparatuses. When speaking of purely theoretical
calculation we mean calculation based only on the general lows of physics
without using any data obtained by experimental measurements in packed bed