Page 101 - Percolation Models for Transport in Porous Media With
P. 101
94 CHAPTER 5. NON-STEADY STATE TWO-PHASE FLOW
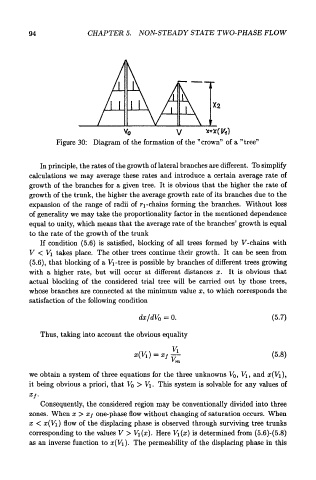
Figure 30: Diagram of the formation of the "crown" of a "tree"
In principle, the rates of the growth of lateral branches are different. To simplify
calculations we may average these rates and introduce a certain average rate of
growth of the branches for a given tree. It is obvious that the higher the rate of
growth of the trunk, the higher the average growth rate of its branches due to the
expansion of the range of radii of r 1-chains forming the branches. Without loss
of generality we may take the proportionality factor in the mentioned dependence
equal to unity, which means that the average rate of the branches' growth is equal
to the rate of the growth of the trunk
If condition {5.6) is satisfied, blocking of all trees formed by V-chains with
V < V1 takes place. The other trees continue their growth. It can be seen from
{5.6), that blocking of a V 1-tree is possible by branches of different trees growing
with a higher rate, but will occur at different distances x. It is obvious that
actual blocking of the considered trial tree will be carried out by those trees,
whose branches are connected at the minimum value x, to which corresponds the
satisfaction of the following condition
dxfdV 0 = 0. {5.7)
Thus, taking into account the obvious equality
(5.8)
we obtain a system of three equations for the three unknowns V 0 , V1 , and x(Vt),
it being obvious a priori, that V 0 > V1 • This system is solvable for any values of
Xf·
Consequently, the considered region may be conventionally divided into three
zones. When x > x 1 one-phase flow without changing of saturation occurs. When
x < x(Vt) flow of the displacing phase is observed through surviving tree trunks
corresponding to the values V > Vt(x). Here V 1{x) is determined from (5.6)-{5.8)
as an inverse function to x(Vi). The permeability of the displacing phase in this