Page 134 - Performance Leadership
P. 134
Chapter 8 Balancing Performance and Risk • 123
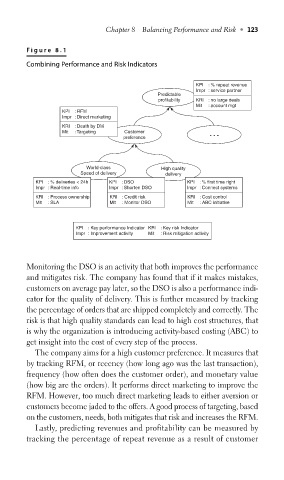
F igur e 8.1
Combining Performance and Risk Indicators
KPI : % repeat revenue
Impr : service partner
Predictable
profitability KRI : no large deals
Mit : account mgt
KPI : RFM
Impr : Direct marketing
KRI : Death by DM
Mit : Targeting Customer . . .
preference
World-class High quality
Speed of delivery delivery
KPI : % deliveries < 24h KPI : DSO KPI : % first time right
Impr : Real-time info Impr : Shorten DSO Impr : Connect systems
KRI : Process ownership KRI : Credit risk KRI : Cost control
Mit : SLA Mit : Monitor DSO Mit : ABC initiative
KPI : Key performance Indicator KRI : Key risk Indicator
Impr : Improvement activity Mit : Risk mitigation activity
Monitoring the DSO is an activity that both improves the performance
and mitigates risk. The company has found that if it makes mistakes,
customers on average pay later, so the DSO is also a performance indi-
cator for the quality of delivery. This is further measured by tracking
the percentage of orders that are shipped completely and correctly. The
risk is that high quality standards can lead to high cost structures, that
is why the organization is introducing activity-based costing (ABC) to
get insight into the cost of every step of the process.
The company aims for a high customer preference. It measures that
by tracking RFM, or recency (how long ago was the last transaction),
frequency (how often does the customer order), and monetary value
(how big are the orders). It performs direct marketing to improve the
RFM. However, too much direct marketing leads to either aversion or
customers become jaded to the offers. A good process of targeting, based
on the customers, needs, both mitigates that risk and increases the RFM.
Lastly, predicting revenues and profitability can be measured by
tracking the percentage of repeat revenue as a result of customer