Page 149 - Performance Leadership
P. 149
138 • Part III Principles from the Values and Social Dimensions
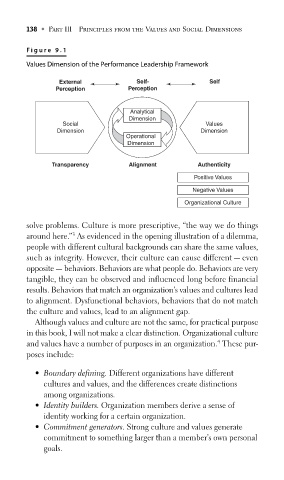
F igur e 9.1
Values Dimension of the Performance Leadership Framework
External Self- Self
Perception Perception
Analytical
Dimension
Social Values
Dimension Dimension
Operational
Dimension
Transparency Alignment Authenticity
Positive Values
Negative Values
Organizational Culture
solve problems. Culture is more prescriptive, “the way we do things
3
around here.” As evidenced in the opening illustration of a dilemma,
people with different cultural backgrounds can share the same values,
such as integrity. However, their culture can cause different—even
opposite—behaviors. Behaviors are what people do. Behaviors are very
tangible, they can be observed and influenced long before financial
results. Behaviors that match an organization’s values and cultures lead
to alignment. Dysfunctional behaviors, behaviors that do not match
the culture and values, lead to an alignment gap.
Although values and culture are not the same, for practical purpose
in this book, I will not make a clear distinction. Organizational culture
4
and values have a number of purposes in an organization. These pur-
poses include:
• Boundary defining. Different organizations have different
cultures and values, and the differences create distinctions
among organizations.
• Identity builders. Organization members derive a sense of
identity working for a certain organization.
• Commitment generators. Strong culture and values generate
commitment to something larger than a member’s own personal
goals.