Page 123 - Petroleum and Gas Field Processing
P. 123
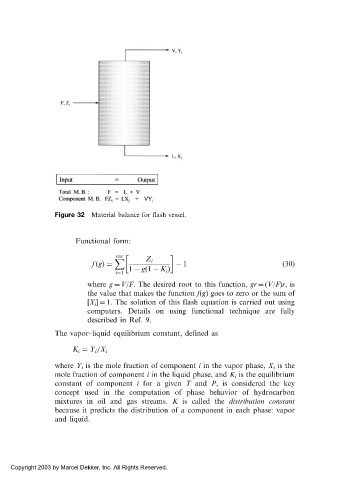
Figure 32 Material balance for flash vessel.
Functional form:
i¼c
Z i
X
f ðgÞ¼ 1 ð30Þ
1 gð1 K i Þ
i¼1
where g ¼ V/F. The desired root to this function, gr ¼ (V/F)r,is
the value that makes the function f(g) goes to zero or the sum of
[X i ] ¼ 1. The solution of this flash equation is carried out using
computers. Details on using functional technique are fully
described in Ref. 9.
The vapor–liquid equilibrium constant, defined as
K i ¼ Y i =X i
where Y i is the mole fraction of component i in the vapor phase, X i is the
mole fraction of component i in the liquid phase, and K i is the equilibrium
constant of component i for a given T and P, is considered the key
concept used in the computation of phase behavior of hydrocarbon
mixtures in oil and gas streams. K is called the distribution constant
because it predicts the distribution of a component in each phase: vapor
and liquid.
Copyright 2003 by Marcel Dekker, Inc. All Rights Reserved.