Page 120 - Petroleum and Gas Field Processing
P. 120
3. Stain test: It is rather an old test (formerly named the
‘‘handkerchief ’’ test). It simply consists of holding and exposing
a white cloth in the gas stream leaving the separator. The
performance of the separator is considered acceptable if a brown
strain does not form on the cloth in 1 min.
3.9 FLASH CALCULATIONS
3.9.1 Introduction
The problem of separating the gas from crude oil for well fluids (crude oil
mixtures) breaks down to the well-known problem of flashing a partially
vaporized feed mixture into two streams: vapor and liquid. In the first
case, we use a gas–oil separator; in the second case, we use what we call a
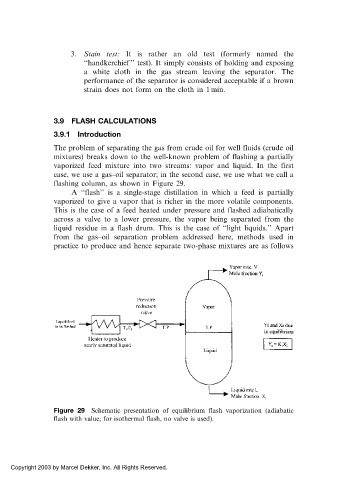
flashing column, as shown in Figure 29.
A ‘‘flash’’ is a single-stage distillation in which a feed is partially
vaporized to give a vapor that is richer in the more volatile components.
This is the case of a feed heated under pressure and flashed adiabatically
across a valve to a lower pressure, the vapor being separated from the
liquid residue in a flash drum. This is the case of ‘‘light liquids.’’ Apart
from the gas–oil separation problem addressed here, methods used in
practice to produce and hence separate two-phase mixtures are as follows
Figure 29 Schematic presentation of equilibrium flash vaporization (adiabatic
flash with value; for isothermal flash, no valve is used).
Copyright 2003 by Marcel Dekker, Inc. All Rights Reserved.