Page 176 - Petrophysics 2E
P. 176
PERMEABILITY-POROSITY RELATIONSHIPS 149
-
1000
(I)
a
> -
ai
*
m
>
g 100
er
a
M
M
2
n
'0
C
48 10
e!
a
M
t
L
1
0 001 0 01 01 1 10 100 1 ow
Time, hrs
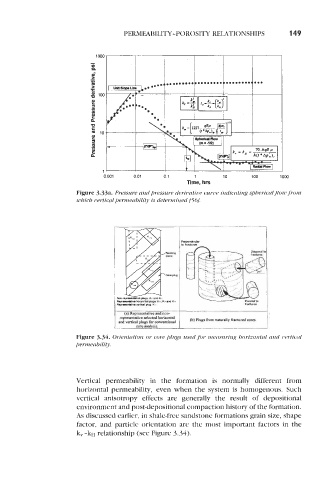
Figure 3.33a. Pressure and pressure derivative curve indicating spherical pow from
which vertical permeability is determined [56].
(a) Representative and non-
representative selected horizontal
and vertical plugs for conventional @)Plugs from naturally fractured cores.
core analysis.
Figure 3.34. Orientation or core plugs used for measuring horizontal and vertical
permeability.
Vertical permeability in the formation is normally different from
horizontal permeability, even when the system is homogenous. Such
vertical anisotropy effects are generally the result of depositional
environment and postdepositional compaction history of the formation.
As discussed earlier, in shale-free sandstone formations grain size, shape
factor, and particle orientation are the most important factors in the
k,-kH relationship (see Figure 3.34).