Page 267 - Petrophysics 2E
P. 267
240 PETROPHYSICS: RESERVOIR ROCK PROPERTIES
formation [ 191. Silica cement, however, tends to distort qualitatively
and quantitatively the texture-controlled permeability distribution of
sand beds. In the loosely packed sandstones, packing appears to have
little or no effect on this permeability distribution. In consolidated
sandstones, the effect of packing on permeability distribution is
considerable.
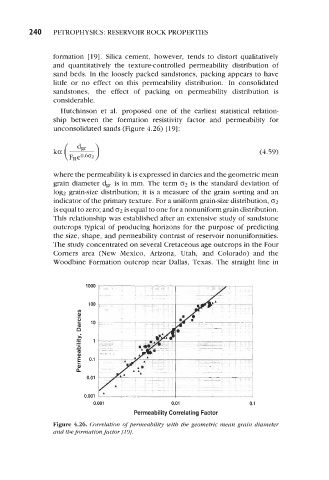
Hutchinson et al. proposed one of the earliest statistical relation-
ship between the formation resistivity factor and permeability for
unconsolidated sands (Figure 4.26) [ 191 :
(4.59)
where the permeability k is expressed in darcies and the geometric mean
grain diameter dgr is in mm. The term (32 is the standard deviation of
log;! grain-size distribution; it is a measure of the grain sorting and an
indicator of the primary texture. For a uniform grain-size distribution, (32
is equal to zero; and 02 is equal to one for a nonuniform grain distribution.
This relationship was established after an extensive study of sandstone
outcrops typical of producing horizons for the purpose of predicting
the size, shape, and permeability contrast of reservoir nonuniformities.
The study concentrated on several Cretaceous age outcrops in the Four
Corners area (New Mexico, Arizona, Utah, and Colorado) and the
Woodbine Formation outcrop near Dallas, Texas. The straight line in
lo00
100
.-
u)
Q
$ IO
0
.= 1
5;
-
.-
P
m
Q
E 0.1
z
n
0.01
0.001
0.001 0.01 0.1
Permeability Correlating Factor
Figure 4.26. Correlation of permeabilility with the geometric mean grain diameter
and the formation factor [IPJ.